LABORATORY RFID SOLUTIONS
Integrated RFID identification and tracking solutions for laboratories
Chemical and temperature resistant RFID labels to withstand harsh environments and ensure accuracy, reliability, and efficiency in the lab. With Computype’s proven automatic ID solutions, you can streamline your workflow through improved data management. RFID technology helps ensure the proper connectivity and communication of samples, compounds, biologics, reagents, and other laboratory assets with their associated platforms.

RFID-enabled sample tracking and management
Enhance your identification and tracking strategy with custom-engineered RFID inlays and labels, robust encoding printers, and compatible readers to support your processes and workflows.
Some of the primary advantages of using RFID include increased data storage, automated data logging, enhanced sample tracking, increased read capabilities, and improved security measures.
So, how can you implement RFID in your lab?
With the many variables impacting successful RFID integration in the lab, our RFID experts are here to help you understand your needs and goals and design a solution that is assured to meet your requirements.
How can RFID add value to your lab?
RFID can enable you to quickly and wirelessly locate your samples and specimens, secure and capture sensitive data, confirm authorized suppliers, and gain tighter control over your most critical assets. RFID can store much more information with much larger data storage capacities than barcodes. Additionally, RFID allows information to be updated which will enable you to track the expiration date and automatically update information.

locating samples
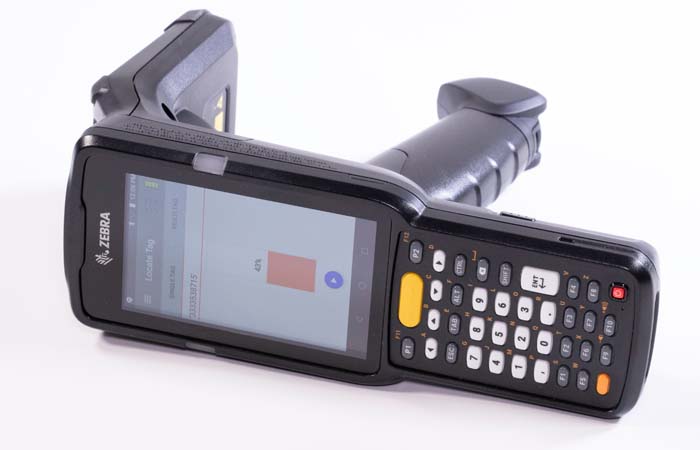
RFID can enable location-based sample tracking, making it possible to locate an individual sample or reagent within a collection. Handheld readers paired with UHF inlays can help guide you directly to a specific item quickly and confidently, reducing the time spent looking for lost samples.

authentication
Many specialized reagents and other consumables are proprietary, designed only for use in specific automated instruments. RFID security and encryption can be used to authenticate reagents and disable operations if unauthorized reagents or evidence of tampering are detected.
automated data logging
If specimens require stable environmental conditions during storage and processing, RFID sensors can be used to automatically record data history and update the information at regular intervals. RFID can act as the memory of the sample and record variables that fall outside specific parameters.
Which assets can you tag in your lab?
RFID tags and labels can be engineered for several common pieces of labware including tubes and vials, microwell plates, bottles, and microscope slides; as well as sample racks and storage boxes.
Some assets may be more challenging to tag than others, for instance if the asset is very small or when liquid may be causing interference with the tag, but we welcome those opportunities and can often develop a suitable solution.
Wondering if your laboratory is a good fit for RFID? Reach out today to schedule your free consultation with one of our experts.
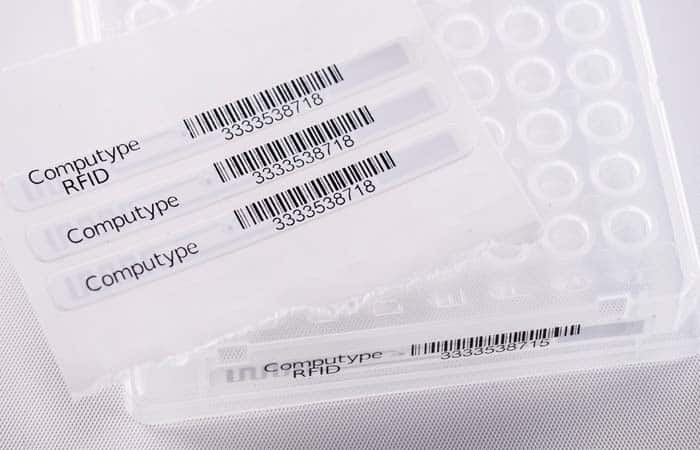
RFID tracking solutions components and variables
Although every RFID solution will look a bit different, they all still have the same basic components. Our experts are there to help integrate each of these components and provide you with a comprehensive, functional solution. We’ll source all necessary equipment, and compatible software and work with you through the entire process from conception through post-installation service and upgrades.
1
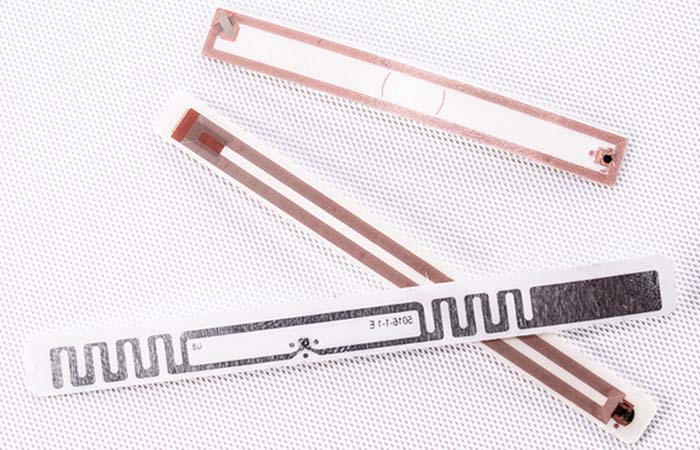
RFID Tags and Labels
RFID tags and labels can enhance tracking abilities, increase data capacity, and make your labels more functional by including supplementary text and barcodes.
2
RFID Enabled Printing
RFID-enabled printers encode an RFID tag with variable values. These encoding printers can print barcode images and text as well to create a multi-functional label.
3
Readers and Antennas
Readers and antennas transmit radio waves and convert those waves into data. The antenna and reader are often combined into a single device for laboratory solutions.
4
Integrated Data & Software
Software and middleware can be used to integrate the tag data into your existing systems, perform ID lookups, drive encoding printers, and more.
RFID hybrid, multi-functional labels to enhance communication
Barcodes still have an important role to play in identification and tracking. In fact, RFID and barcodes can work together in complementary ways. Adding RFID to your traditional labels can offer you three communication channels: the data stored in the tag’s chip, the barcode, as well as printed human-readable information.
This three-way combination satisfies several requirements:
- Branding can be color-correct and reproduced to a high standard
- The product name, important safety information, and any additional information required by law or regulation can be visibly presented
- The barcode identifier will provide data if RFID is not available, and the same information will be replicated on the RFID tag
- The RFID component also allows the label to be updated to record any processes the labeled product passes through
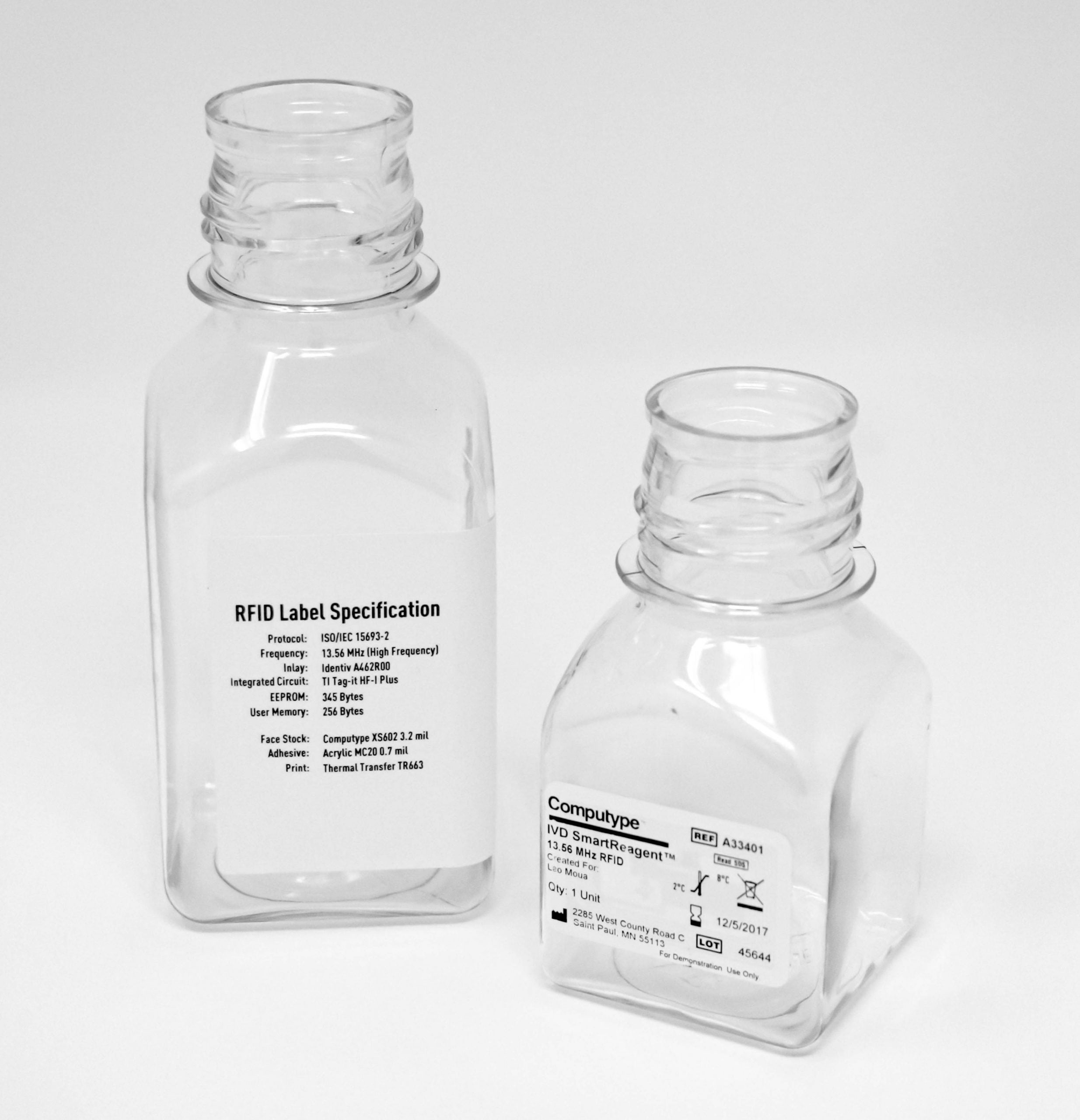
RFID inlay frequencies: UHF, HF, and NFC
RFID-enhanced labels have specific properties based on the type of tags and the frequency on which they operate. Operating frequencies are measured in hertz (typically megahertz) and are categorized into three main types: Low Frequency, High Frequency, and Ultra High Frequency. Low Frequency tags will not be commonly found in a laboratory environment, so we will focus primarily on HF and UHF. Within the High Frequency band, you’ll also find NFC, or Near Field Communication. You’ve likely encountered NFC at stores or restaurants when you tap to pay with your credit card or smartphone.
HF vs UHF for Laboratories
One of the first things we need to determine when designing an RFID solution for a customer is whether we need to engineer High Frequency or Ultra-High Frequency inlays.
Both the encoding printer and the reader/antenna need to be compatible with the frequency type, and certain models may only be compatible with UHF inlays, or only with HF inlays.
Determining whether your lab requires HF or UHF tags depends on many variables including the size and type of asset you’re tagging, whether liquids are involved, where your tags will be read, etc.
Our goal is to make sure that we understand what you’re tagging, how you’ll handle your tagged assets, your environment, and most importantly, your larger business objectives to ensure that we provide a comprehensive solution that will add value to your lab.

Print and encode simultaneously with RFID-enabled printers
As RFID increases in popularity, more and more barcode label printers are being introduced with encoding abilities—let’s take a look at a few we commonly recommend due to their abilities to accommodate a range of needs and perform to a high standard:
ZEBRA RFID Printers
UHF Preferred: Zebra ZD and ZT

Zebra offers a wide array of RFID-enabled printers suitable for use in the lab. While most labs will require the compact design found in the ZD series due to their limited desktop space, the ZT series provides the printing power needed to support 24/7 large batch printing.
SATO RFID Printers
HF Preferred: Sato CL4NX

The Sato CL4NX has long been a favorite of ours, and remains our preferred model for encoding HF and NFC tags. This model can easily handle high print volumes, the aluminum outer casting makes it ideal for harsh environments, and the in-line scan and verify feature ensures viable barcodes.
RFID coupling and reader communication
Coupling refers to the method used to link or “couple” the RFID tag and reader/antenna to one another. This needs to be done in order for the reader to recognize and retrieve information from the tag. The two primary types of coupling in an RFID system are inductive and radiative coupling. Whether inductive or radiative coupling are used typically depends on the frequency level of the tag.
Desktop vs Handheld Readers
When it comes to readers, there are different reasons why you may want a specific type of reader, and different reasons why you may require a specific type of reader.
The two categories of readers are desktop readers (or pad readers) and handheld readers. Desktop readers are stationary, the tagged asset needs to travel to the reader in order for the data to be read. Handheld readers are mobile, in this case the reader is the component that needs to travel to the tagged asset.
Handheld readers are extremely helpful for locating samples, whereas desktop or pad readers are more successful in a workstation or positioned along a conveyor.
Depending on the required frequency type of your inlays, you may be limited on what type of reader you can use in your lab. While desktop readers can communicate with both HF and UHF tags, handheld readers are used solely with UHF tags.








