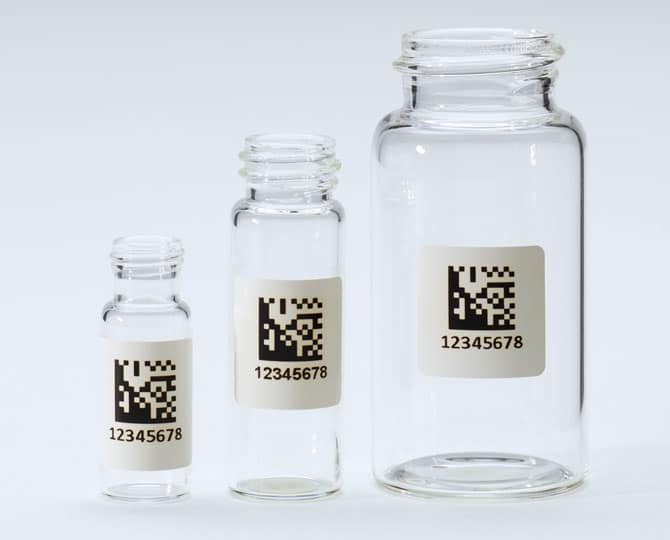
What is Data Matrix?
A Data Matrix barcode is a two-dimensional matrix barcode that has gained prominence in laboratories and various industries for its compact design and high data capacity. Unlike traditional linear barcodes that store data only horizontally, Data Matrix barcodes can store information both horizontally and vertically, allowing for the efficient encoding of data.
In laboratories, Data Matrix barcodes serve as a robust method for identifying and tracking items. They consist of black squares arranged in a square or rectangular pattern on a white background. The arrangement of these squares represents encoded data, which can include alphanumeric characters, numbers, or other information.
The data capacity of a Data Matrix barcode can vary depending on the version and size of the code. The smallest version, known as the “10×10,” can hold up to 1,400 numeric characters or 311 alphanumeric characters. As the size of the code increases, so does its data capacity, with larger versions capable of encoding even more data.
Data Matrix barcodes come in multiple symbol versions, each tailored to specific data capacity and size requirements. Common versions include ECC 200, ECC 000-140, ECC 050, and ECC 080. Laboratories can choose the appropriate symbol version based on the amount of data to be encoded and the available space for labeling.
Additionally, data matrix barcodes often incorporate error correction codes, such as Reed-Solomon codes, which enhance their robustness. These error correction codes allow for the reconstruction of data even if part of the barcode is damaged or unreadable.
This feature is crucial for maintaining data integrity, especially in lab environments where labels may be exposed to various conditions.
Data Matrix barcodes are designed for high-speed scanning, making them easily readable by barcode scanners and imaging devices. This quick and accurate scanning capability is essential for efficient data capture in laboratory workflows.
Their compact size makes them suitable for labeling small labware and samples, while their ability to store a substantial amount of data ensures that crucial information is readily accessible.
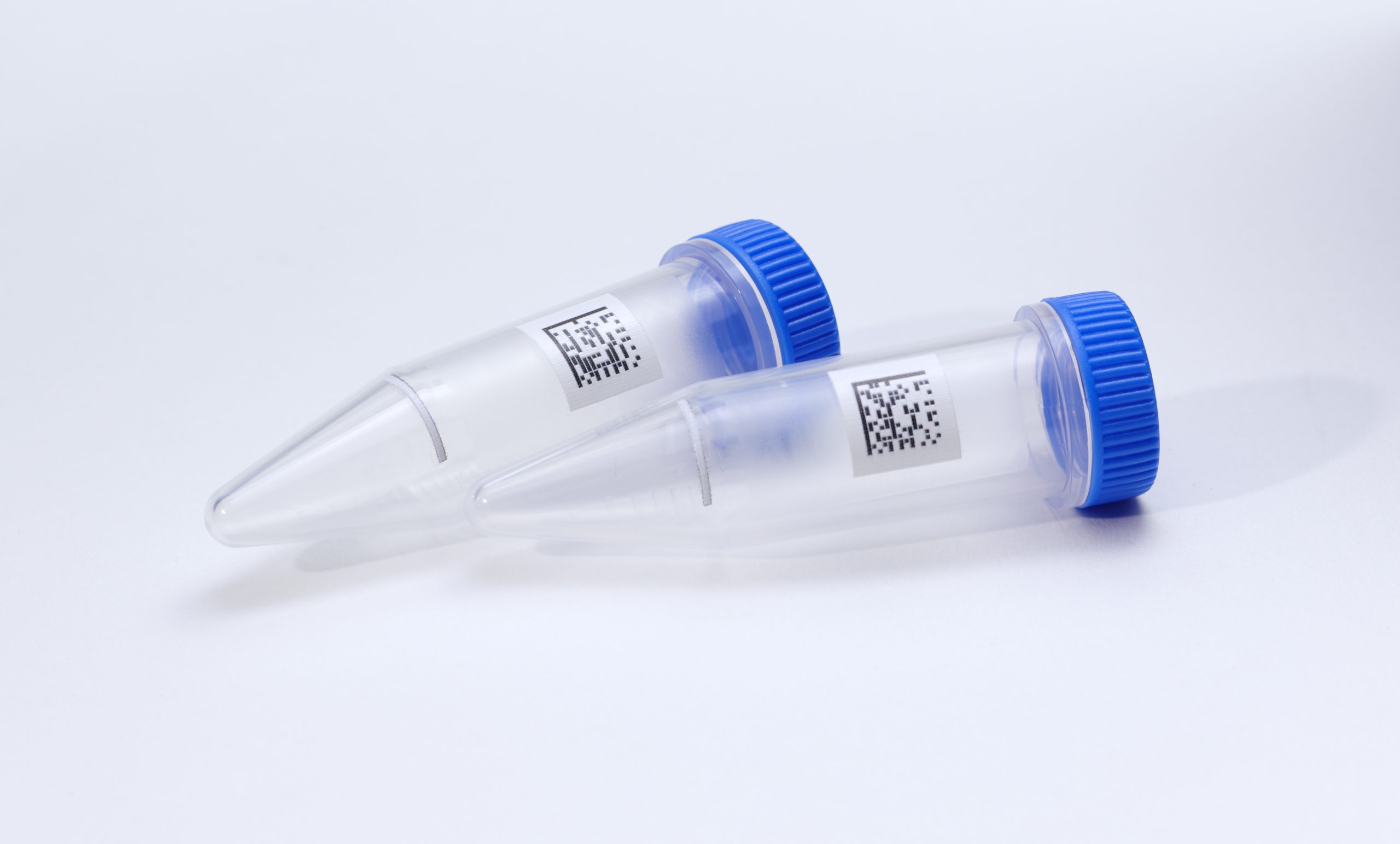
GS1 Data Matrix
GS1 Data Matrix is a specialized type of data matrix barcode that adheres to specific industry standards set by GS1, a global organization dedicated to developing and maintaining supply chain standards. These standards encompass various aspects of product identification, labeling, and data encoding. Some key standards that GS1 Data Matrix adheres to include:
- Global Trade Item Numbers (GTINs): GS1 Data Matrix encodes product information using GTINs, which are globally unique identifiers for products. These numbers follow specific formats and rules set by GS1 to ensure uniqueness and consistency.
- Application Identifiers (AIs): AIs are prefixes that define the type of data encoded within the barcode. GS1 has a standardized list of AIs for various data elements like batch/lot numbers, expiration dates, and serial numbers.
- Data Encoding Rules: GS1 provides guidelines on how specific data elements should be encoded within the GS1 Data Matrix. For example, it specifies the format for encoding dates and specific characters for data delimiters.
- Supply Chain Traceability: GS1 standards emphasize traceability in the supply chain, ensuring that products and their components can be tracked accurately from production to consumption. GS1 Data Matrix is designed to support this traceability.
- Data Structure: GS1 Data Matrix has a structured format for consistently encoding data elements, making it easier for businesses to exchange and interpret information correctly.
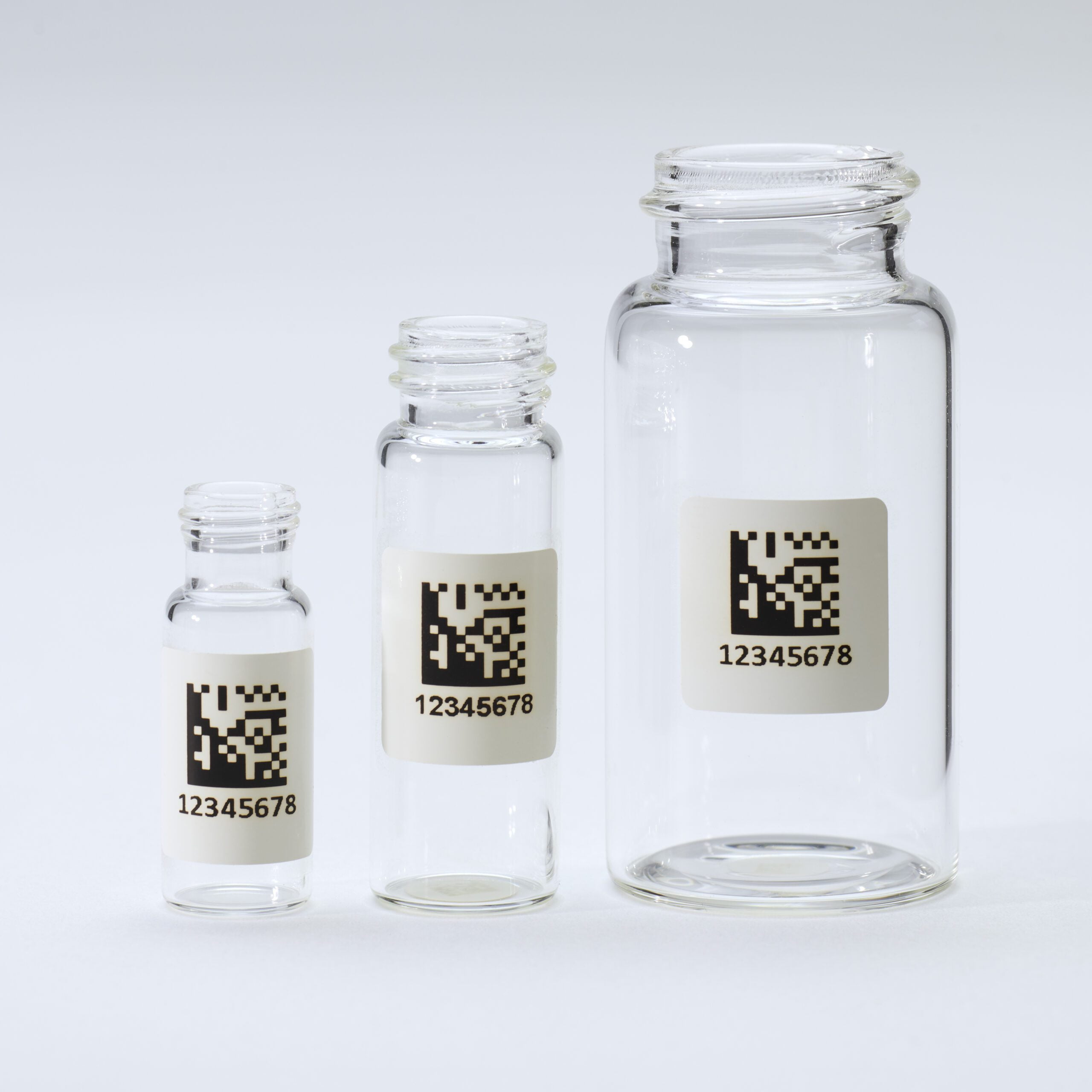

Adhering to these specific GS1 standards aims to achieve uniformity, interoperability, and accuracy in data encoding and exchange, particularly in healthcare, retail, and manufacturing industries. It ensures that businesses and organizations can work together seamlessly and that product information is consistently and accurately represented in GS1 Data Matrix barcodes.
Because GS1 Data Matrix is a globally recognized standard, sharing data with other labs, suppliers, or stakeholders in the supply chain is easier. This is particularly valuable for labs involved in collaborative research or those that need to share sample information with external partners.
Additionally many labs, especially those in healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and food testing, must adhere to regulatory standards that mandate accurate tracking and labeling of samples. GS1 Data Matrix helps labs comply with these standards, such as UDI (Unique Device Identification) for medical devices and pharmaceutical serialization requirements.
Data Matrix Codes in Laboratories
Laboratories across various industries utilize Data Matrix barcodes, including both GS1 Data Matrix and regular Data Matrix, for a range of critical applications. These 2D barcodes play a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency, data accuracy, and traceability within laboratory operations. Here’s how Data Matrix is employed in laboratory settings.
- Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Many laboratories, particularly in healthcare, pharmaceuticals, and food testing, must adhere to strict regulatory standards. GS1 Data Matrix is commonly used to meet these requirements, such as Unique Device Identification (UDI) for medical devices and serialization for pharmaceuticals. Compliance ensures the accurate tracking and reporting of critical information. - Data Exchange and Collaboration
Labs often collaborate with external partners, suppliers, and other research institutions. Data Matrix barcodes facilitate data exchange by encoding information electronically. This simplifies the sharing of sample information, experimental data, and results, ensuring that all stakeholders can work seamlessly together. - High Data Density and Efficiency
Both GS1 Data Matrix and regular Data Matrix offer high data density, allowing a significant amount of information to be stored in a compact space. Their efficient scanning capabilities reduce the risk of errors associated with manual data entry, contributing to data accuracy and operational efficiency. - Custom Data Encoding
Regular Data Matrix is particularly versatile in laboratory settings as it can encode custom data according to specific research needs. This flexibility makes it suitable for a wide range of applications beyond standardized traceability requirements.
Empowering Biopharmaceuticals with Data Matrix
Biopharmaceutical laboratories specializing in developing and producing biological products such as vaccines, monoclonal antibodies, and gene therapies rely extensively on Data Matrix barcodes, including GS1 Data Matrix and regular Data Matrix, to meet unique industry requirements.
Data Matrix barcodes enable precise traceability of pharmaceutical products throughout their lifecycle, ensuring compliance with strict regulatory requirements like the FDA’s Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA). Moreover, their ability to accommodate serial numbers aids in combating counterfeiting and ensuring product authenticity. These features make Data Matrix barcodes an essential tool for businesses providing identification and tracking solutions in the biopharma sector, contributing to data accuracy, product integrity, and overall operational efficiency.

Data Matrix Labware Compatibility
In research, clinical, and environmental laboratories, precise sample identification and traceability are paramount. Data Matrix codes are affixed to sample containers, vials, and specimens. They encode information such as sample type, origin, and other relevant data. This ensures that each sample is accurately identified, tracked, and associated with its corresponding data throughout the testing and analysis process.
The versatility of Data Matrix barcodes extends beyond their data capacity and compact size; it also lies in their compatibility with a wide range of labware types. When implementing Data Matrix codes in laboratory settings, several considerations come into play:
Size and Placement: For smaller labware items like PCR tubes and strips or tissue cassettes, which have limited labeling space, the compact size of Data Matrix barcodes is ideal. They can be placed in areas where space is limited, ensuring minimal interference with other labeling or information on the labware.
Pairing Data Matrix with Linear Codes: Laboratories often opt for a combination of Data Matrix and linear codes on a single piece of labware. For instance, on a test tube, a linear code can be placed along the side for quick item recognition, while a Data Matrix barcode on the bottom or cap provides additional information, such as batch numbers or sample details. This dual-coding approach ensures both ease of identification and comprehensive data capture.
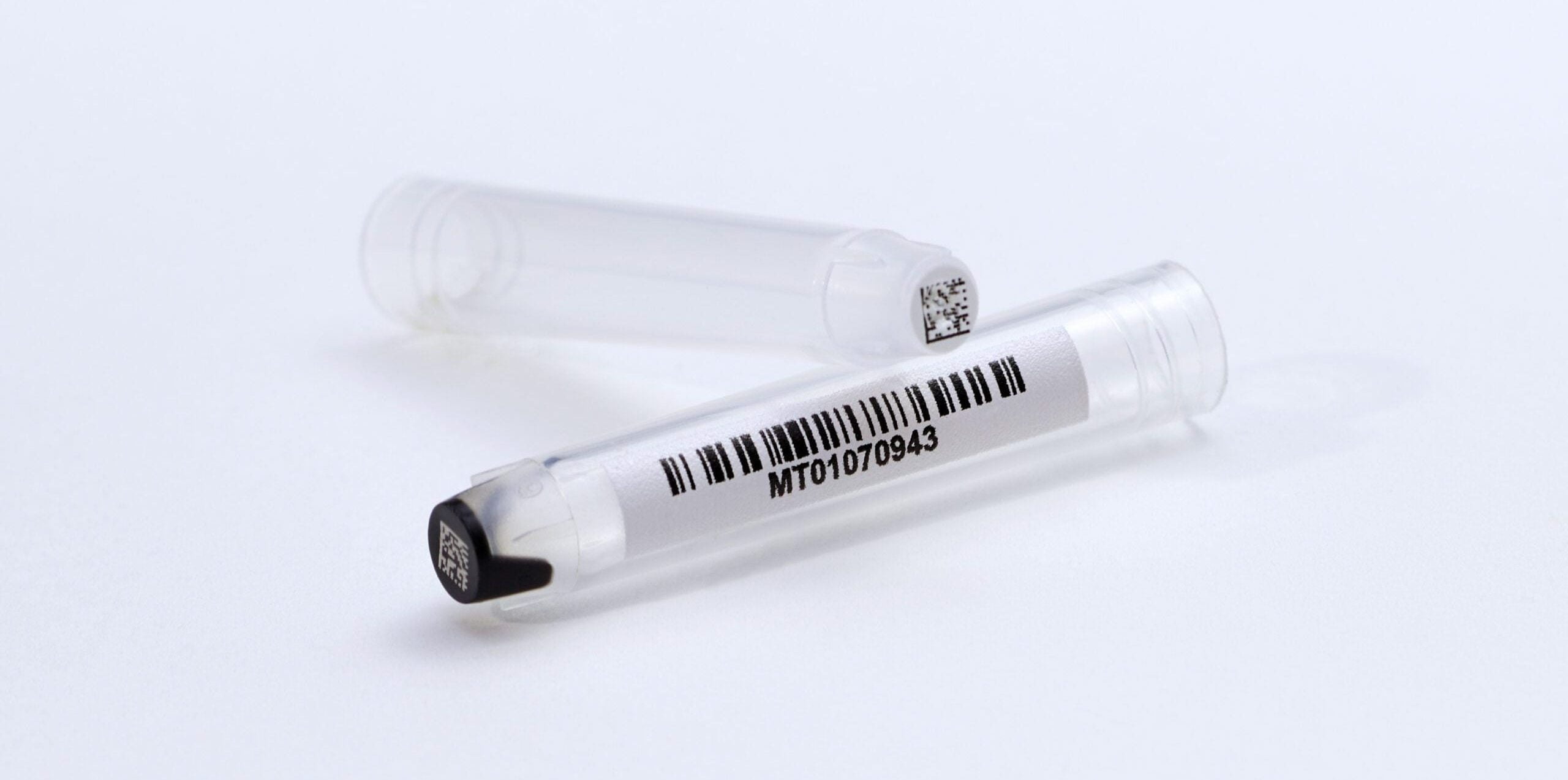
Ensuring Readability: Regardless of the labware type, ensuring the readability of Data Matrix barcodes is essential. Proper printing methods, such as thermal transfer printing or laser marking, should be employed to generate clear and durable barcodes. Additionally, the placement of the code should consider the orientation of the labware during scanning to facilitate easy and accurate reading.
The growing popularity of Data Matrix barcodes in laboratories is a testament to their effectiveness in addressing modern identification and tracking challenges. Their enhanced data capacity, compact size, automation benefits, regulatory compliance, sample traceability, and versatility make them a valuable asset in the pursuit of efficiency, accuracy, and data integrity in laboratory operations.
In conclusion, the adoption of Data Matrix barcodes is a trend that reflects the evolving needs of laboratories in the digital age, where data accuracy and efficiency are essential for scientific advancements and research breakthroughs.

