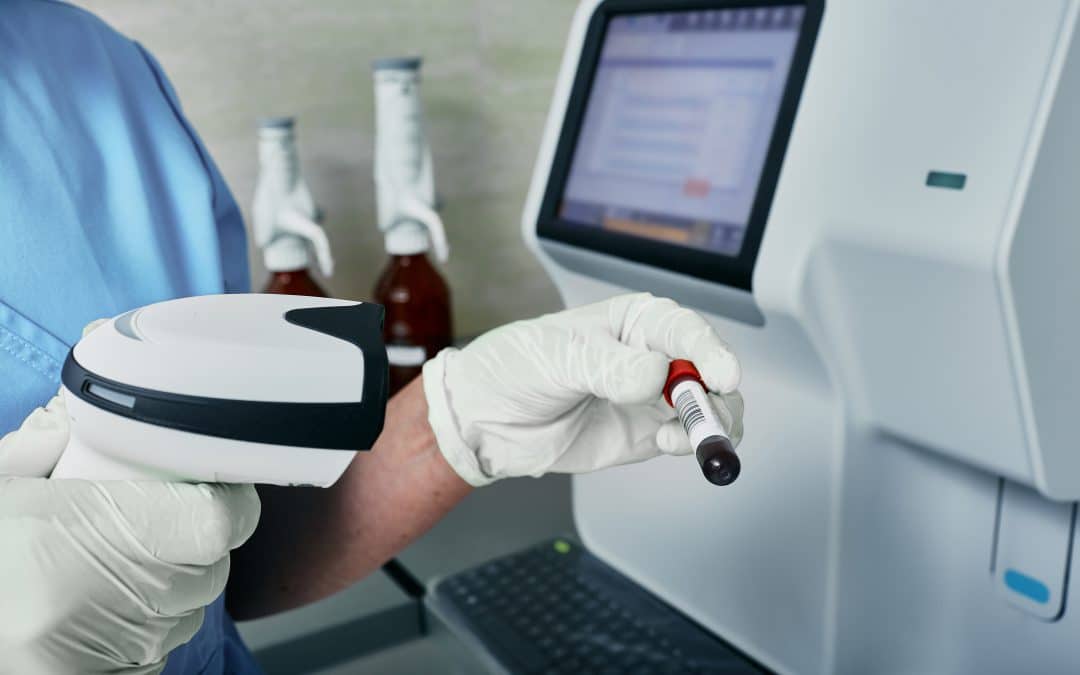
In the dynamic landscape of laboratory operations, precision and efficiency are paramount. Handheld barcode scanners have emerged as indispensable tools, streamlining processes and enhancing data accuracy. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the different types of handheld barcode scanners, delve into the intricacies of 1D and 2D scanners, discuss desirable qualities, highlight potential pitfalls, and showcase examples from Zebra Technologies. Ultimately, we’ll uncover why handheld barcode scanners are invaluable assets in laboratory settings.
Types of Barcode Scanners
Barcode scanners come in various types to cater to different business needs. Laser barcode scanners use a laser beam to read barcodes quickly and accurately, making them ideal for high-volume scanning in retail and manufacturing. 2D imaging scanners, on the other hand, capture images of entire barcodes and can read both 1D and 2D codes, offering versatility for applications like healthcare and retail. Now, let’s delve into these two types in more detail:
Laser Barcode Scanners: Laser barcode scanners are designed for precision and speed. They work by emitting a laser beam that reflects off the barcode and is captured by a light-sensitive sensor. The scanner then deciphers the reflected light to decode the information contained in the barcode. These scanners excel in high-volume environments, where fast and accurate scanning is crucial. They are commonly used in retail for point-of-sale transactions and in manufacturing and logistics for efficient inventory tracking.
2D Imaging Scanners: 2D imaging scanners, also known as area imagers, are highly versatile. They capture an image of the entire barcode using a camera or sensor array and then employ specialized software to decode the information. Unlike laser scanners, they can read both 1D and 2D barcodes, including QR codes. This versatility makes them valuable in various industries, including healthcare for patient identification, document management for scanning documents with barcodes, and retail for decoding QR codes on mobile devices. 2D imaging scanners are preferred when flexibility in barcode reading angles and orientations is required.
Key Features to Ensure Successful Scans
When selecting handheld barcode scanners for laboratory use, certain key features apply to both 1D and 2D scanners.
- Scan Speed: Choose scanners with high-speed capabilities to maintain operational efficiency.
- Connectivity Options: Ensure scanners have reliable connectivity options compatible with existing systems.
- Durability: Prioritize durable scanners capable of withstanding the demanding lab environment.
- Software Compatibility: Select scanners that seamlessly integrate with existing laboratory management software.
- Regular Maintenance: Establish a routine maintenance schedule, including cleaning the scanner and updating firmware, to prevent performance issues.
Potential Pitfalls to Avoid
Being aware of potential pitfalls is equally important in making informed decisions. Poor print quality can affect barcode readability, leading to errors in data capture. Compatibility issues may arise if the chosen scanner is not compatible with existing software or systems, leading to integration challenges. Lack of user training can result in errors and inefficiencies, emphasizing the importance of comprehensive training programs to ensure staff proficiency with the scanners.
Why Laboratories Use Handheld Barcode Scanners
In laboratory settings, handheld barcode scanners play a transformative role. They facilitate accurate and efficient tracking of individual samples, ensuring precise data entry and reducing the risk of errors. Laboratories leverage these scanners for the organization and management of supplies, such as reagents and consumables, contributing to streamlined processes and efficient workflows. The scanners also contribute to enhanced data accuracy, a critical factor in scientific research. Additionally, the swift identification and tracking of laboratory equipment further enhance efficiency in daily operations, ensuring that equipment is utilized optimally.
Zebra Scanners
Zebra Technologies offers exemplary handheld barcode scanners that cater to a range of needs. The Zebra LS2208, a high-performance 1D scanner, is ideal for swift tasks such as inventory management and equipment identification. Its durability ensures longevity in demanding laboratory environments. The Zebra DS2200 Series, with both 1D and 2D capabilities, excels in complex data capture tasks and adaptive scanning. Its versatility makes it suitable for diverse applications within laboratory settings.
In the landscape of barcode scanning, exemplary devices like the Zebra LS2208 play a pivotal role. Engineered by Zebra Technologies, a leader in automatic identification solutions, the LS2208 is a prime example of a 1D barcode scanner that excels in various laboratory applications.
The Zebra LS2208 boasts the following features:
- Rapid Scanning: With a high-performance scan rate, the LS2208 ensures swift and accurate data capture, making it ideal for applications where speed is essential, such as inventory management.
- Durable Design: Built to withstand the rigors of daily use, the LS2208 is known for its robust construction. Its durable design ensures longevity in demanding environments, providing a reliable solution for continuous scanning needs within laboratories.
- Ease of Use: Featuring a user-friendly design, the LS2208 is easy to operate, reducing the learning curve for users. This is particularly important in fast-paced laboratory settings where efficiency is crucial.
Taking identification and tracking to the next level, Zebra’s DS2200 series stands out as a prime example of versatile barcode scanners suitable for intricate tasks in laboratories.
The DS2200 series encompasses both 1D and 2D scanning capabilities, providing a comprehensive solution for various applications. Key features include:
- Data Versatility: With the ability to read both 1D and 2D barcodes, including QR codes, the DS2200 series offers enhanced data versatility. Laboratories can leverage this capability for tracking complex samples, managing multiple data points, and ensuring a broader range of identification possibilities.
- Rapid and Accurate Scanning: Similar to its 1D counterpart, the DS2200 series maintains a high-performance scan rate, ensuring rapid and accurate data capture. This is crucial for efficiency in tasks that demand precision, such as sample tracking and inventory management.
- Adaptive Scanning Technology: The DS2200 series incorporates adaptive scanning technology, allowing it to excel in varying lighting conditions. This ensures reliable performance even in environments with suboptimal lighting, a common consideration in laboratory settings.
- User-Friendly Design: Building on Zebra’s commitment to user-friendly design, the DS2200 series is easy to use, making it accessible to a wide range of users. Intuitive operation reduces the likelihood of errors during scanning, contributing to overall operational efficiency.
In conclusion, handheld barcode scanners, exemplified by Zebra LS2208 and DS2200 series, are indispensable assets in laboratories, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and overall productivity.